Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is a protocol that enables hosts to receive multicast traffic from a multicast group. For a host to be allowed to receive Cisco IGMP messages encapsulated in IP datagrams from multicast groups, it has to support Cisco IGMP and the router interface that it terminates to, because if not, the request will be discarded.
There are three versions of IGMP that are elaborated by RFC 1112. The first version is already considered obsolete and will not be further discussed. IGMPv2 is defined by RFC 2236 as the most widely used version among multicast networks, and lastly, IGMPv3, which is according to RFC3376, is used by Source-Specific Multicast (SSM).
The diagram below shows an architecture of multicast-based communication using IGMP. The multicast client initially sends a request for membership to an IP multicast group via its local multicast routers. The router always is listening for requests and then periodically forwards subscription queries.
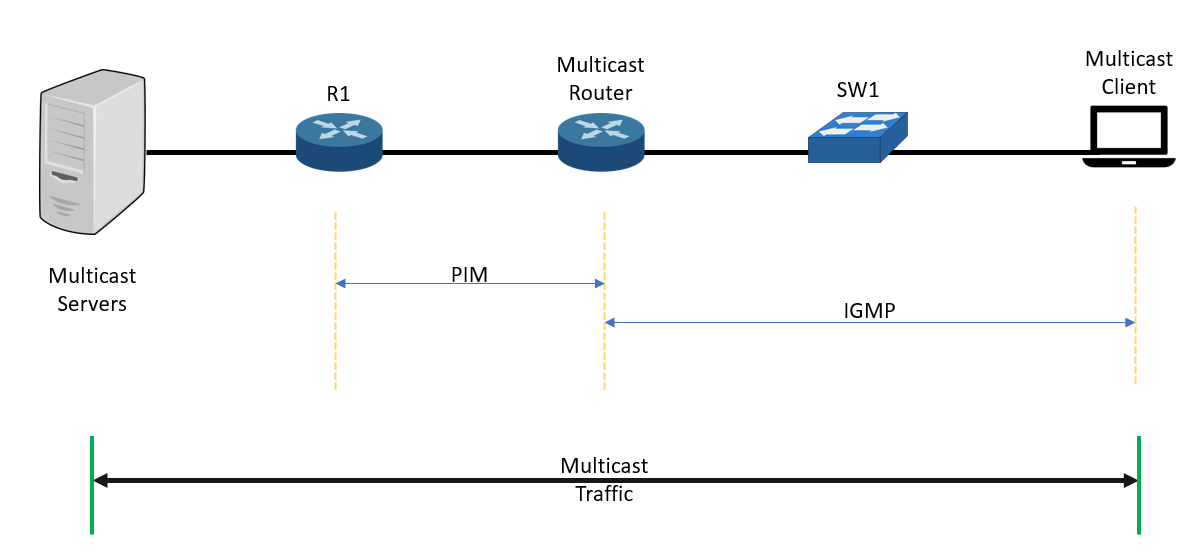
The Switch analyzes Cisco IGMP related information and identifies IGMP transactions. R1 and the Multicast Router uses Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) within the LAN of the Multicast client to guide the multicast traffic towards the Multicast Server. IGMP does enable multicast routing that operates at the Network Layer, which is like how ICMP is. IGMP snooping is used to reduce multicast flooding on a LAN segment.
IGMPv2
IGMP version 2 is an improvement of the now obsolete first version but has a significant feature with the addition of leave group message. This IGMP leave message enables the host to communicate with the local multicast router and let it know that it wants to leave the multicast group.
Once it receives the leave group message, the router sends out a query specific to the group and checks if there are any hosts interested in receiving the traffic. If there are no replies, the multicast router times out and halts sending IGMP queries. With this enhancement, IGMPv2 significantly reduces the leave latency and prevents unwanted traffic compared to IGMPv1.
The IGMPv2 message format is illustrated below. The IGMPv2 message is encapsulated in IP protocol version 2. According to Cisco, the messages are sent with the IP router alert option set, which indicates that the packets should be examined more closely, and a time-to-live (TTL) of 1.
TTL is an 8-bit field in an IP packet header that is set by the sender of the IP packet and decremented by every router on the route to its destination. If the TTL reaches 0 before reaching the destination, the packet is discarded. IGMP packets are sent with a TTL of 1 so that packets are processed by the local router and not forwarded by any router.
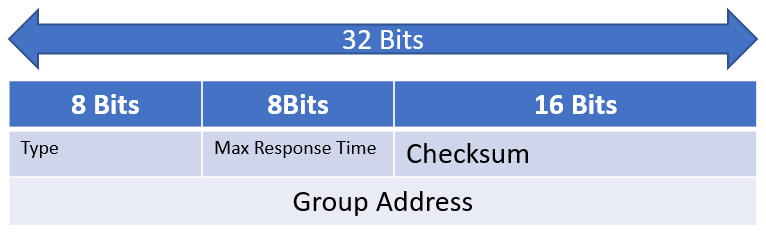
Listed below are the IGMPv2 Message format fields:
- General Membership Query
- Group-specific Query
- Version 1 Membership Report
- Version 2 Membership Report
- Leave Group
- Checksum
- Max Response Time
- Multicast Group Address
IGMPv3
IP IGMP version 3 is backward compatible with both IGMPv1 and IGMPv2, but unlike the older versions, IGMPv3 supports IP multicast source filtering, enabling the receivers to choose the source they prefer to accept the multicast traffic from. The advantage of IGMPv3 is that it added new fields for membership query and introduced a new IGMP message type named Version 3 membership report to support source filtering.
IGMPv3 Modes
IGMP version 3 enables receivers’ signal membership to a group address utilizing the two modes below as defined by RFC 3376:
- MODE_IS_INCLUDE – indicates that the interface has a filter-mode of INCLUDE for the specified multicast address. The Source Address fields in this Group Record contain the interface’s source list for the specified multicast address if it is non-empty.
- MODE_IS_EXCLUDE – indicates that the interface has a filter-mode of EXCLUDE for the specified multicast address. The Source Address fields in this Group Record contain the interface’s source list for the specified multicast address if it is non-empty.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:
