As wireless networks grow, more centralized controllers will be participating in providing coverage over a wider area, making mobility solutions significant. Mobility or roaming services enables a WLAN client to retain its association seamlessly while moving from one Access Point to another. Cisco WLAN controllers (WLC) can be organized into wireless mobility groups to support intercontroller roaming.
A mobility group is a set of WLCs defining a seamless roaming area for a wireless client. The controllers within the same mobility group dynamically exchange information and forward client traffic when an intercontroller roaming occurs.
They also share the client’s context and state and their list of Access Points to ensure that each other’s Access Points are not regarded as rogue devices. This information allows the network to enable WLAN intercontroller roaming and WLC redundancy. The mobility group also restricts the distribution of a client’s security context data and limits Access Point fail-over between WLCs.
Wireless client devices can efficiently roam between two centralized WLCs that are configured to be in the same mobility group in the wireless network. Both Layer 2 and Layer 3 intercontroller roaming are supported. Secure caching is supported, including Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM), key caching, and 802.11r credential caching.
A client device can still roam to a different controller in different mobility groups, but it is inefficient. The credentials are neither cached nor shared, so the client must perform complete authentication when roaming.
Mobility List
As seen in the image below, mobility groups have an underlying structure. Every WLC keeps a mobility list with its own MAC address and other WLCs’ MAC addresses, and a mobility group name is allocated to each group. A controller can be configured in a single mobility group only.
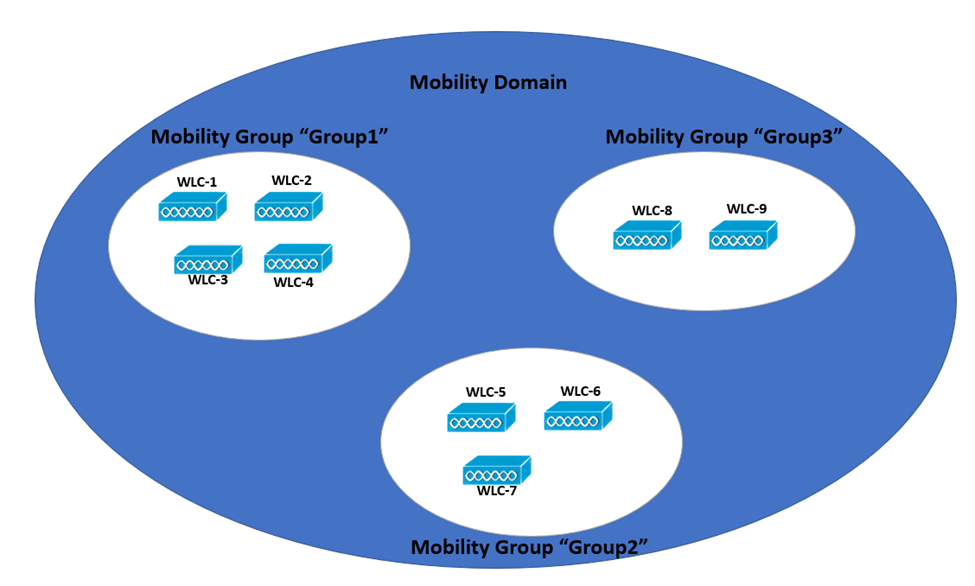
The mobility list provides a controller with a viewpoint of the outside world. It will be aware of and trusts only the other WLC configured in the mobility list. If two WLCs are not on each other’s mobility list, they are unaware of each other, and the wireless clients cannot roam between them. The clients will then have to associate and authenticate from the start.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:
