The traditional campus network architecture can not fully address the current network needs. Cisco Software-Defined Access (SDA) is a relatively recent technology that extends virtualization to the network’s access layer. Cisco SDA improves campus networks by leveraging the following functions:
- Network Automation: SDA enables centralized network device management using Cisco Digital Network Architecture (DNA) Center, simplifying network design, provisioning, and deployment.
- Network Assurance and Analysis: SDA uses telemetry to predict network and security risks proactively.
- Host Mobility: Cisco SD-Access enables wired and wireless clients’ host mobility.
- Identity Services: Cisco ISE (Identity Services Engine) identifies connected devices and users. It also provides contextual information required to implement network segmentation and access control security policies.
- Policy Enforcement: Application and access policies are created based on group-based policies using Security Group Access Control Lists (SGACLs), a simpler and more scalable form of identity-based policy enforcement.
- Secure Segmentation: Network segmentation is easier with the SD-Access solution. It supports segmentation for guests, corporate, facilities, and IoT-enabled infrastructure.
- Network Virtualization: Single physical infrastructure can support multiple Virtual Networks (VNs) with distinctive access policies.
Software Defined Access Main Components
Cisco SD-Access has two main components, which are:
- Cisco Campus Fabric Solution – includes the features and protocols of the control, data, management, and policy planes to operate the network infrastructure.
- Cisco DNA Center – manages Cisco Campus Fabric Solution to be considered SD-Access.
Cisco SDA Architecture
The Cisco SD-Access architecture has four layers, the physical layer, the network layer, the controller layer, and the management layer.
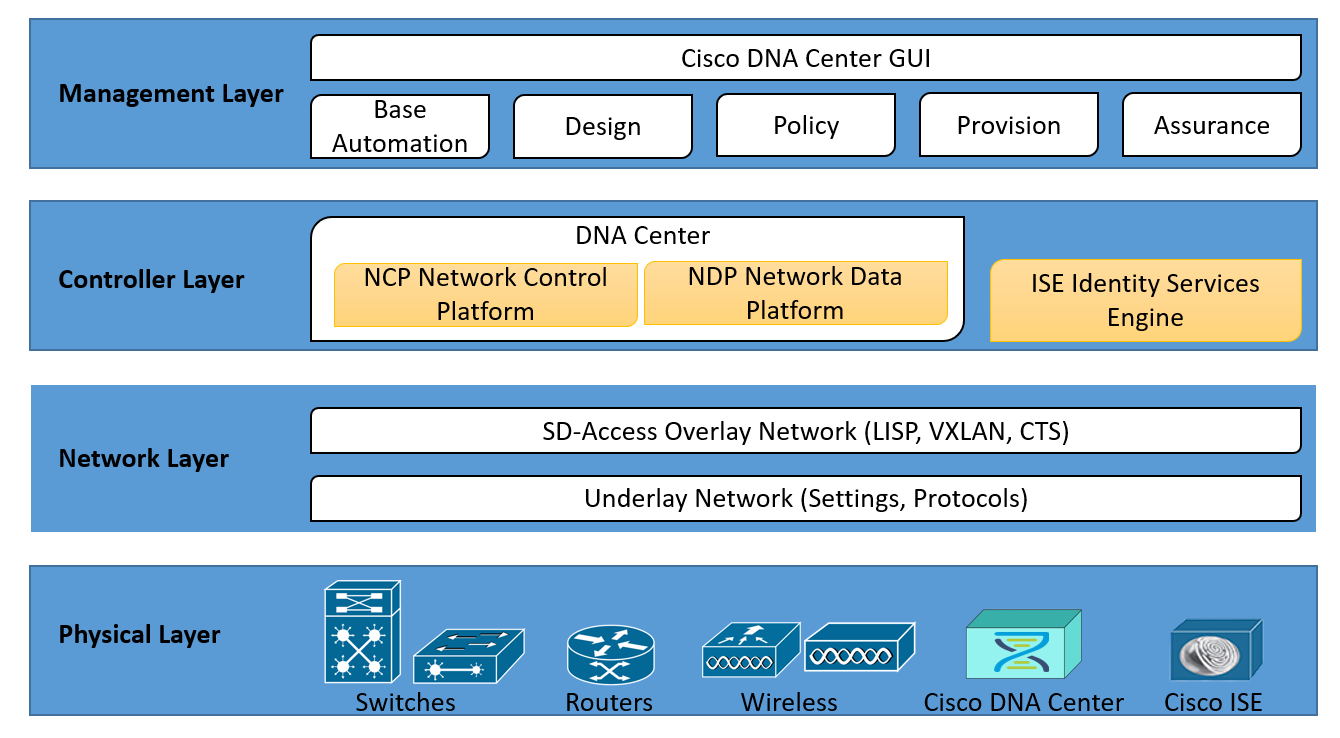
Cisco SDA Architecture: Physical Layer
Cisco SDA runs on top of the physical network elements, such as routers, switches, servers, WLAN Controllers, and Wireless Access Points. The network devices that participate in the SD-Access network fabric should support the hardware Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), and the software requirements of the SDA network layer.
Cisco access switches that are part of the SDA fabric because of automation but don’t actively participate are called SD-Access extension nodes.
The physical layer devices of the SD-Access fabric are as follows:
- Switches – provide wired (LAN) connectivity to the fabric. Catalyst and Nexus Cisco switches are supported.
- Routers – enable WAN and branch connectivity to the SDA fabric. Cisco ASR, ISR, and CSR routers are supported. Cisco CSRv and ISRv virtual network routers are also supported.
- Controller Appliances – SD-Access requires the Cisco DNA Center and Cisco ISE controller appliances.
- Wireless – provides connectivity from wireless networks (WLANs) to the fabric through Cisco WLCs and Wireless APs.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:
