The underlay network and the overlay network make up the Cisco Software-Defined Access (SDA) network layer. These sublayers operate together to send and receive data packets between network devices participating in the Cisco SD-Access. The controller layer has access to all of the network layer information.
The image below illustrates the relationship between the underlay network and the overlay network:
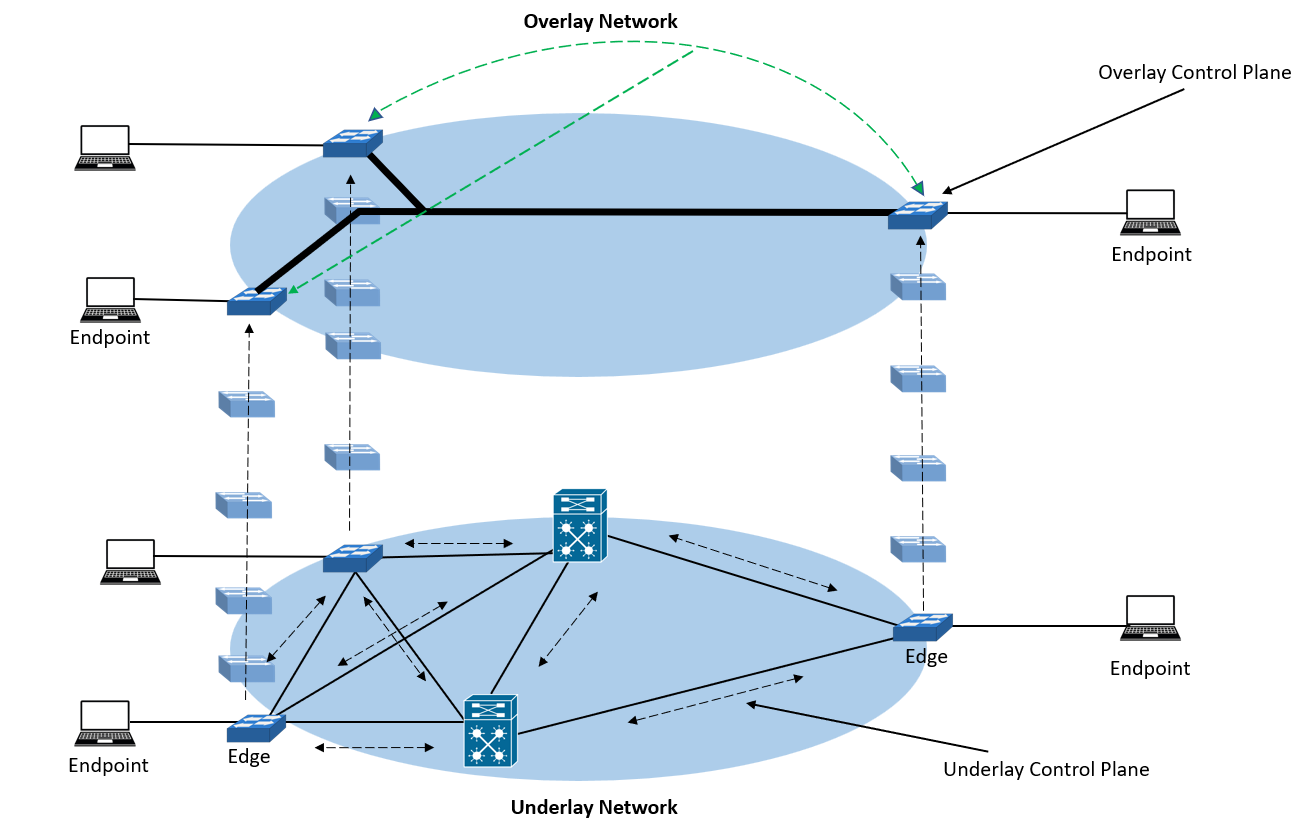
Underlay Network
The underlay network comprises the underlying physical layer. It transports data packets between network devices in the SD-Access fabric overlay. Therefore, the underlay network should be configured to guarantee performance, scalability, and High Availability (HA) so that it will not negatively affect the SDA fabric overlay.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) can be used in a Layer 2 underlay network design, but it is not recommended. Instead, using Layer 3 routed network access campus design using the IS-IS IGP is preferred since IS-IS provides neighbor establishment without IP dependencies, peering capability utilizing loopback IP addresses, and address-agnostic traffic. The underlay network supports two models, manual underlay and automated underlay.
Manual Underlay
The manual underlay network is manually configured and managed using CLI or API. It enables network customization to accommodate particular design needs, such as using OSPF as the IGP. It also allows SDA to run on top of a legacy or a third-party IP-based network.
Automated Underlay
The Cisco DNA Center Local Area Network Automation feature fully controls and orchestrates the automated underlay network, which creates an IS-IS routed access campus design. Cisco DNA Center’s LAN Automation utilizes the Cisco Network Plug and Play features to deploy unicast and multicast routing configurations in the underlay network, significantly improving SD-Access traffic delivery efficiency.
The automated underlay network reduces misconfigurations and simplifies the network underlay creation. However, it does not allow manual network customization for special design requirements.
Overlay Network (SD-Access Fabric)
The overlay network is the SD-Access fabric. It is a virtual and tunneled network that interconnects the network devices virtually, forming an SDA fabric. It enables policy-based network segmentation, wired and wireless networks’ host mobility, and better network security than traditional networks’ switching and routing capabilities. It also overcomes the underlay network’s complexity and constraints.
The overlay network is fully automated, whether the underlay network model is manual or automated. The SD-Access fabric includes all the essential overlay control plane addressing and protocols. It also contains the global configurations needed in the SD-Access fabric operation.
The overlay network is based on various existing technologies. Cisco SD-Access solution is powerful and unique due to the combination of these technologies and Cisco DNA Center automation.
The SD-Access fabric has three basic operation planes: the Control Plane, Data Plane, and Policy Plane.
SD-Access Fabric Control Plane
The SD-Access fabric control plane is based on the Locator/ID Separation Protocol (LISP). LISP eliminates router processing for every IP destination address and route by moving the remote destination information to the LISP Map Server (MS), a centralized mapping database, and a control plane node in SD-Access. The LISP MS allows the routers to manage their local routes and query the map system to locate destination Endpoint Identifiers (EIDs).
It provides SD-Access benefits such as smaller routing tables, dynamic host mobility for wireless and wired network endpoints, and built-in network segmentation via VRF instances. Cisco SD-Access also includes distributed Anycast Gateway, VN Extranet, and Fabric Wireless.
SD-Access Fabric Data Plane
The fabric data plane tunneling is based on Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN). It builds the overlay network for the SD-Access fabric. VXLAN encapsulation is used instead of LISP data encapsulation because it can encapsulate the original Ethernet header and perform MAC-in-IP encapsulation.
With VXLAN, the SD-Access fabric can support Layer 2 and Layer 3 virtual topologies. It can also operate over any IP-based network with built-in network segmentation and group-based policy.
The new VXLAN format is called VXLAN Group Policy Option (VXLAN-GPO) and supports Cisco TrustSec Scalable Group Tags (SGTs). The new fields are added to the first 4 bytes of the VXLAN header to transport up to 64,000 SGT tags.
The following are new fields in the VXLAN-GPO packet format:
- Group Policy ID – a 16-bit identification that carries the SGT tag.
- Group-Based Policy Extension Bit (G Bit) – a 1-bit field that when an SGT tag is contained within the Group Policy ID field, the value is set to 1.
- Don’t Learn Bit (D Bit) – a 1-bit field that is set to 1 if the egress Virtual Tunnel Endpoint (VTEP) should not learn the encapsulated frame’s source address.
- Policy Applied Bit (A Bit) – a 1-bit field that is only defined when the G bit is set to 1. When set to 1, it means that this packet has previously been subjected to the group policy, and the network devices must apply no additional policies.
SD-Access Fabric Policy Plane
The policy plane is based on Cisco TrustSec, where the SGT tags are assigned to authenticated users and end devices. Network policies are enforced on the SD-Access fabric based on the SGT tags.
TrustSec SGT tags provide various benefits for Cisco SD-Access, including the following:
- Supports network-based segmentation utilizing Virtual Networks (VNs) and group-based segmentation
- Network address-independent group-based policies are based on SGT tags, which are simpler
- Dynamic enforcement of group-based policies for wired and wireless traffic
- VXLAN policy constructions across legacy or third-party networks
- Policy enforcement is extended to external networks, such as cloud or data center networks, using SGT Exchange Protocol (SXP) to transfer tags
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:
