There are six OSPF LSA types used for IPv4 routing, which include:
- Type 1 (Router LSA) – Generated and advertised by routers within a common area.
- Type 2 (Network LSA) – It advertises multi-access network segments attached to the Designated Router (DR).
- Type 3 (Summary LSA) – Generated by the Area Border Router (ABR), and it advertises network prefixes originating from different areas.
- Type 4 (Summary ASBR LSA) – Generated by ABR. It advertises a summary LSA for a specific Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR) for other routers to find it.
- Type 5 (AS External LSA) – Generated by the ASBR. It advertises LSAs for redistributed routes.
- Type 7 (NSSA External LSA) – A not-so-stubby area doesn’t allow type 5 LSAs, so type 7 LSAs are generated instead. It advertises NSSA redistributed routes.
LSA Sequence Number
The Link State Advertisement sequence number is a 32-bit number that solves issues brought on by network LSA propagation delays. The LSA sequence number is incremented whenever the originating router transmits LSAs. A router processes an LSA if the received LSA sequence number is greater than the LSA sequence in the Link State Database (LSDB). However, the router discards the LSA if the LSA sequence is lower than the one found in the LSDB.
LSA Age
The OSPF LSA age is entered in the local LSDB and the age value increments by 1 every second. If a router’s LSA age exceeds 1800 seconds or 30 minutes, the originating router advertises a new LSA with an age of 0.
The LSA is declared invalid and removed from the LSDB when its age hits 3600. The repeated flooding of LSAs is considered a secondary safety measure that makes sure all OSPF routers in an area keep a constant LSDB.
OSPF LSA Types
The LSAs for an OSPF area are identical in all routers in that area. Each OSPF area has its own set of LSAs, which the ABRs maintain. The OSPF LSA output can be viewed using the ‘show ip ospf database’ command. The significant OSPF LSA types 1, 2, and 3 are discussed below.
Type 1: Router
The type 1 LSAs are the LSDB’s fundamental building blocks, and every OSPF router advertises them. There is a type 1 LSA record for every OSPF-enabled link. In the image below, type 1 LSAs are not advertised outside of Area 1, which indicates that an area’s underlying topology is hidden from other areas.
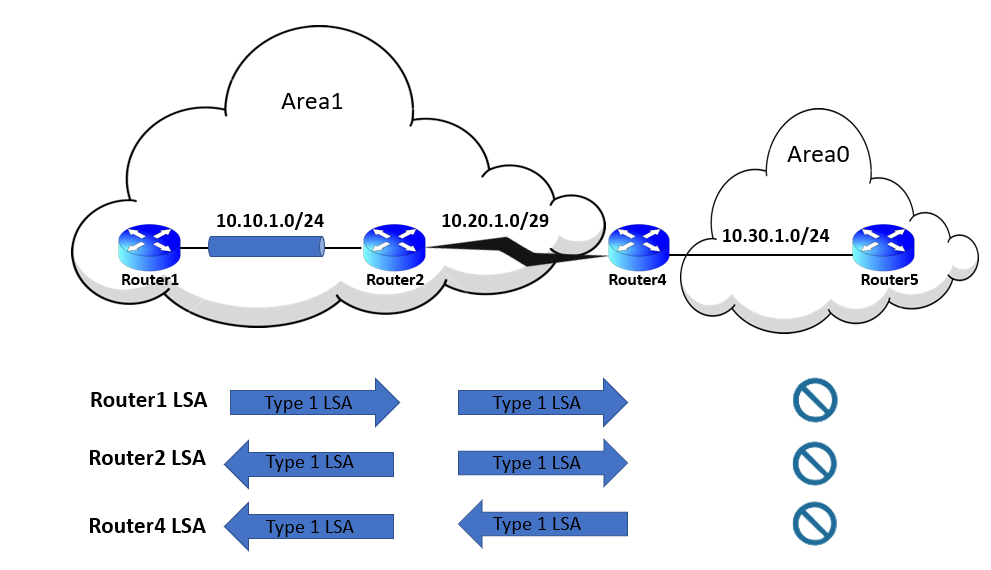
Each type 1 LSA’s initial fields include a Router ID (RID) that includes the following information:
- LSA advertising router
- LSA age
- LSA sequence
- Link count
- Link ID
Type 2: Network
The DR always advertises the type 2 LSA and specifies all the routers connected to that network segment, which is what a type 2 LSA represents. A type 2 LSA is excluded from the LSDB if a DR has not been elected since the corresponding type 1 LSA is a stub. The type 2 LSAs are not forwarded outside the OSPF area where they originated.
Type 3: Summary
This OSPF LSA type represents networks from different areas. The ABRs’ responsibility is to take part in various OSPF areas and make sure that networks associated with type 1 LSAs may be accessed in non-originating OSPF areas.
Again, ABRs do not forward type 1 and type 2 LSAs into other areas. As a result, if an ABR receives a type 1 LSA, it will create a type 3 LSA that references the network in the original type 1 LSA. The type 2 LSA is then used to identify the network mask of the multi-access network. The ABR then advertises the type 3 LSA in other areas.
An ABR regenerates a new type 3 LSA for the non-backbone area if it receives a type 3 LSA from the backbone or Area 0. Then, it identifies itself as the advertising router with the additional cost metric.
The type 3 LSAs appear in the relevant areas. The command ‘show ip ospf database summary‘ displays the type 3 LSA details. The type 3 LSA contains the following:
- Link-state ID or network number
- Subnet mask
- Advertising ABR’s IP address
- Network prefix metric
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:
