A Cisco proprietary advanced Layer 3 IP switching technology called Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) was developed to be up to date on the fast-paced demand of our ever-evolving network structures. Since the 1990’s Cisco Express Forwarding operation has been the default switching mechanism used whenever it requires packet switching operation using the general-purpose CPU on most Cisco platforms that utilized ASIC (Application-specific Integrated Circuit) and network processing units (NPU’s) that requires high packet throughput.
Below are some of the advantages of this switching mechanism:
- Performance improvement.
- Provides network resilience.
- Flexibility and scalability.
Theoretically, Cisco Express Forwarding can be used in any part of the network but is designed to work in a high-performance network that requires high resiliency Layer 3 IP switching. In CEF, the general-purpose CPU functions in software-based and hardware-based routers are different. In software-based routers, the general-purpose CPU handles all the operations, including CEF switching (software CEF), while the hardware-based router does software CEF implemented by specialized ASICs using forwarding engines called the Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) and NPUs (hardware CEF). These forwarding engines enable the router’s packet switching, forwarding, and route lookup capability.
Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM)
The Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) of a switch enables the evaluation and matching in more than one field of a packet. TCAM is an enhanced extension of CAM architecture that allows the processing of upper-layer data like identifying the L2/L3 source/destination IP address, Quality of Service markings, protocol, among other things. An enhancement of TCAM over CAM is that it offers more flexibility in searching using binary. There are three possible search results using TCAM: 0 if it is true, 1 for false, and X, which is a ternary combination that means do not care.
The TCAM entries are stored in VMR format. The V in VMR stands for Value which indicates the fields that should be searched, such as protocol fields and the IP address. The M in VMR is the Mask and it shows the interest and queried fields. The R in VMR is the Result and it specifies the action which matches the Value and Mask that should be taken.
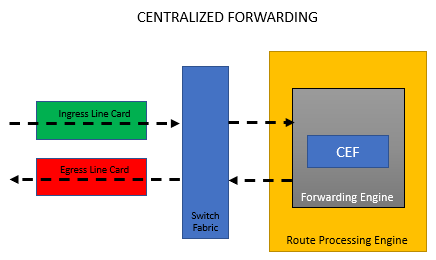
Centralized Forwarding
Since general-purpose CPU is considered cheap, the cost of software-based cisco routers is getting cheaper, but the packet throughput is being sacrificed.
Centralized forwarding architecture happens when packet switching decisions are made when the Route Processor (RP) is equipped with a forwarding engine. A centralized forwarding architecture receives a packet on the ingress line card and is then transmitted to the forwarding engine on the RP. The said packet’s header is then examined by the forwarding engine that decides what port on the egress line card to send it out.
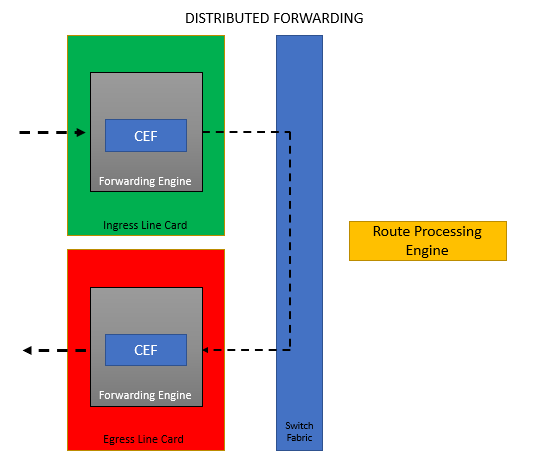
Distributed Forwarding
Distributed forwarding architecture makes its decision independent from the intervention of a Route Processor from an ingress line card that is equipped with forwarding engines. Once a packet is received in the ingress line card, it is then forwarded to the local forwarding engine. A packet lookup is then performed by the forwarding engine. If it determines that the outbound interface is local, the packet is forwarded out the local interface. If the outbound interface is on a different line card, the packet is forwarded all over the switch fabric known as the backplane, directly to the egress line and not passing through the route processor.
Software Cisco Express Forwarding
Software CEF is widely known as Software Forwarding Information Base with the following components below:
- Forwarding Information Base – the FIB is built-in the routing table and contains the next-hop address information for each destination in the network. It stores the mirror image of the forwarding information in the routing table. If a topology or routing happens in the network, the IP routing table is revised and updated. These updates are then reflected in the FIB. CEF utilizes the FIB to make destination IP prefix-based switching decisions.
- Adjacency Table – also known as Adjacency Information Base (AIB) contains the directly connected next-hop IP addresses and their next-hop MAC addresses with the egress interface’s MAC address. The data on the adjacency table is provided from the data gathered from the ARP table or other L2 protocol tables.
Hardware Cisco Express Forwarding
The hardware-based routers require expensive ASICs to design, produce and troubleshoot with limited functionality but enable very high packet rates because they are only programmed for a specific task. Routers can also be equipped with NPU’s as an alternative to ASICs and an advantage is that NPUs are programmable, giving the flexibility to programming and firmware.
According to Cisco, distributed forwarding architectures with hardware CEF allow packet throughput to be greatly increased by offloading packet switching responsibilities to one or more line cards. Packet switching accomplished in distributed platforms is done via dCEF (Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding). dCEF allows CEF data structures to be downloaded to ASICs and the CPUs of all line cards so they can all participate in packet switching. The main advantage of this is switching can be done at a distributed level and increases the packet throughput of the router.
dCEF is a mode of Cisco Express Forwarding operation in which line cards such as Versatile Interface Processor maintain mirror copies of the FIB and adjacency tables. The line cards perform the express forwarding between port adapters; this alleviates the Route Processor of involvement in the switching operation.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training: