The Quality of Service (QoS) marking mechanism differentiates a packet from other packets by modifying the packet’s field or frame header with the following traffic descriptors:
- Internal – QoS groups
- Layer 2 – 802.1Q/p Class of Service (CoS) value
- Layer 2.5 – MPLS Experimental (EXP) bits
- Layer 3 – IP Precedence (IPP) and Differentiated Services Code Points (DSCP) values
The Layer 2 and Layer 3 traffic descriptors are the most commonly used for marking traffic.
Layer 2 QoS Marking
The IEEE 802.1Q standard specifies implementing VLANs in a Layer 2 switched network. It also defines two fields that are placed into the Ethernet frame:
- Tag Protocol Identifier (TPID)
- Tag Control Information (TCI)
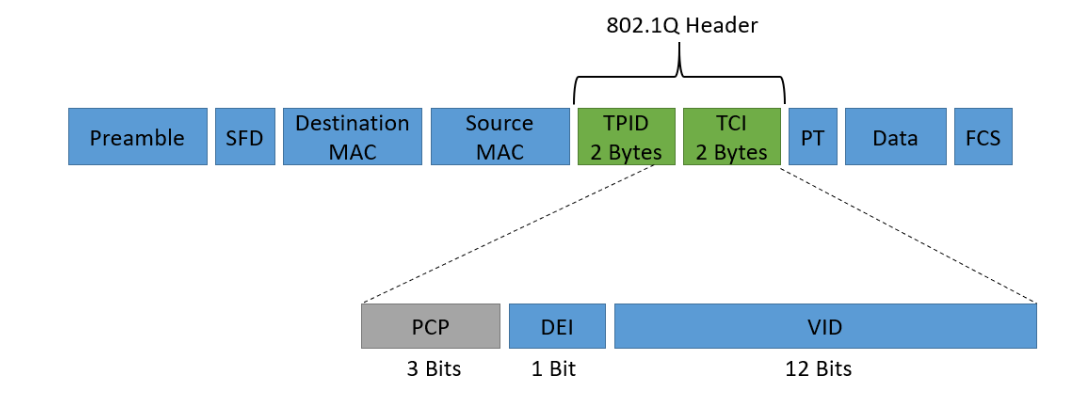
TPID is a 2-byte or 16-bit field with a value of 0x8100, indicating it as an 802.1Q tagged frame. TCI is also a 2-byte or 16-bit field, and it is composed of three fields:
- Priority Code Point (PCP)
- Drop Eligible Indicator (DEI)
- VLAN Identifier (VLAN ID)
Priority Code Point (PCP)
The IEEE 802.1p standard defines the 3-bit field Priority Code Point (PCP). PCP is utilized to mark IP packet headers that belong to a certain CoS. A Layer 2 Ethernet frame can be marked with different priority values using CoS marking:
| PCP Value/Priority | Traffic Type |
| 0(lowest) | Background (BK) |
| 1 (default) | Best effort (BE) |
| 2 | Excellent effort (EE) |
| 3 | Critical applications (CA) |
| 4 | Video with < 100 ms latency and jitter (VI) |
| 5 | Voice with < 10 ms latency and jitter (VO) |
| 6 | Internetwork control (IC) |
| 7 (highest) | Network control (NC) |
When a frame travels over a non-802.1Q link or a Layer 3 network layer header, it loses its CoS marking. Therefore, IP packets must be marked and mapped to additional higher-layer markings to ensure the end-to-end preservation of the CoS values. For instance, the CoS priority levels and the IP Precedence Type of Service (ToS) values in IPv4 can be mapped to each other directly.
Drop Eligible Indicator (DEI)
The 1-bit DEI field can be used individually or in combination with PCP to identify frames that can be dropped during network congestion management. DEI’s default value is 0, meaning the frame is not drop-eligible. A DEI value of 1 means that the frame is drop-eligible.
VLAN Identifier (VLAN ID)
The 12-bit VLAN ID field indicates the VLAN utilized by 802.1Q. The number of VLANs supported by 802.1Q is limited to 4096 since the VLAN ID field only has 12 bits. Therefore, it might not be enough for large networks.
Layer 3 QoS Marking
An IP packet may traverse through non-802.1Q trunked or non-Ethernet links that do not support the CoS field. Layer 3 marking offers a more persistent marking that is retained from the source to the destination.
The IP packet header has an 8-bit Type of Service (ToS) field. The first 3 bits of the ToS field is the IP Precedence (IPP), which is used for marking. The remaining bits are unused. The IPP values are 0 to 7, enabling the network traffic to be partitioned into a maximum of six traffic classes of service. IPP values 6 and 7 are reserved for the internal network.
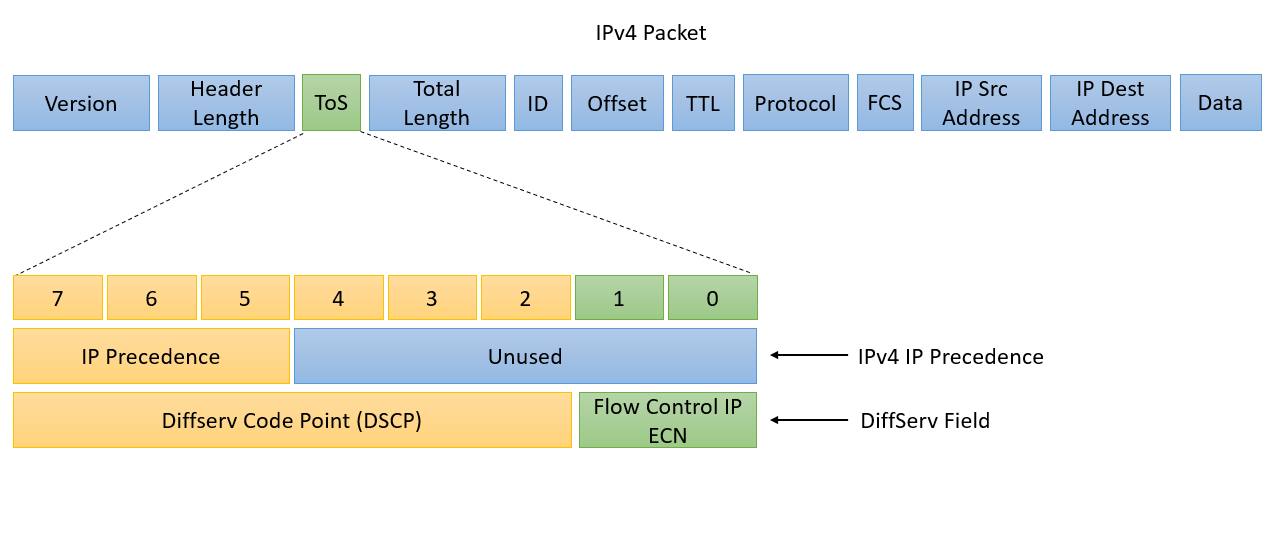
The latest specifications now define the IPv4 ToS and IPv6 Traffic Class fields as the 8-bit Differentiated Services (DiffServ) fields. The DiffServ field is backwards compatible with the IP Precedence value since it uses the same 8 bits originally used for the IPv4 ToS and IPv6 Traffic Class fields.
The DiffServ field is made up of the following fields:
- Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) 2-bit Field
- Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) 6-bit Field
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:
